Transit Gateway Peering Configuration
The Soracom Canal Transit Gateway peering connection connects a Type-F2 VPG to your AWS Transit Gateway. This connection enables bidirectional communication without NAT between devices using IoT SIMs and instances such as EC2 in your Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) over a private network.
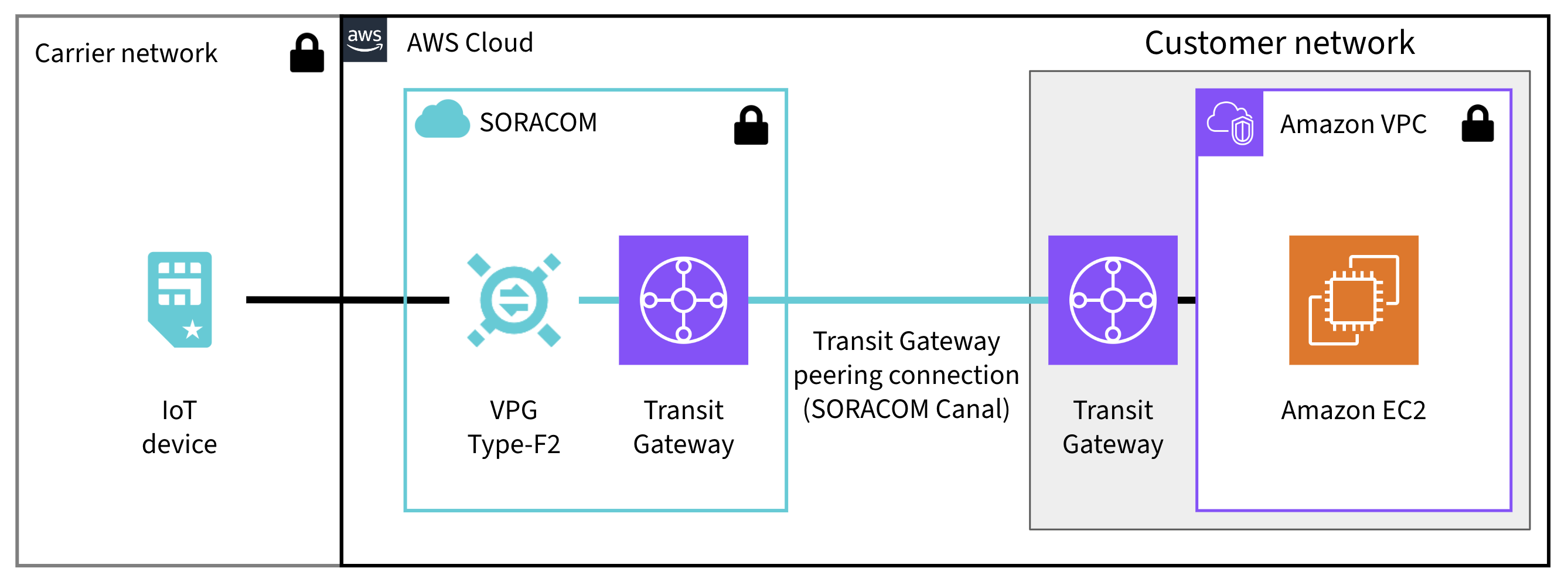
Requirements
To configure Canal with a Transit Gateway peering connection, you will need:
- An AWS Transit Gateway in a region that supports inter-region Transit Gateway peering.
- A Type-F2 VPG. If you haven't already created a VPG, follow the instructions in the Creating a VPG section of this document.
- AWS CLI.
Limitations
If you have created a VPG in Japan coverage, your VPC cannot include the 10.21.0.0/16 IP address range. If your AWS VPC uses a CIDR block that includes this range, you will need to create a new VPC with a CIDR block that does not include this range.
Configuration
Creating a VPG
Creating a VPG will incur fees. Refer to the Pricing & Fee Schedule for more information.
To use a Transit Gateway peering connection, create a Type-F2 VPG.
Follow the instructions from the VPG Type-F2 Configuration documentation to create a new VPG with the following options:
- Type - Select
Type-F2(other VPG types do not support Transit Gateway peering). - Internet gateway - Check Enable internet gateway if you have a requirement to communicate with the internet without sending data through the Transit Gateway. Otherwise, leave this unchecked.
- CIDR Range for device subnet (optional) - The CIDR block of IP addresses assigned to Air and Arc devices that connect to this VPG. If left blank, a default block of
10.128.0.0/9will be used. Manually specified Device Subnets must be within the10.0.0.0/8,172.16.0.0/12, or192.168.0.0/16CIDR ranges and have a subnet mask of/24or larger.
Creating a Transit Gateway
If you have already created a Transit Gateway, you may skip this step.
You can create a Transit Gateway by following these instructions:
-
Log in to the AWS Management Console, click the Services menu, and open the VPC dashboard.
-
In the Region selector, choose the region where your AWS VPC is or will be located.
-
In the navigation menu's Transit gateways section, click Transit gateways.
-
Click Create transit gateway.
-
Configure your transit gateway as desired, ensuring that Default route table propagation is enabled. Then click Create transit gateway. The transit gateway will now be provisioned by AWS.
-
Wait for the Transit Gateway to be provisioned and its state to become Available.
-
In the navigation menu's Transit gateways section, click Transit gateway attachments.
-
Click Create transit gateway attachment.
- Set a descriptive name in the Name tag field, under Transit gateway ID select the transit gateway you just created, and under VPC ID choose your VPC. Then click Create transit gateway attachment.
Creating a Transit Gateway Peering Connection
Create a Transit Gateway peering connection to the Transit Gateway created in Creating a Transit Gateway.
You need the following information about your AWS Transit Gateway to create a Transit Gateway peering connection.
- AWS Region: You can confirm by logging in to the AWS Management Console and checking the region displayed at the top right (e.g., Tokyo).
- AWS Account ID: You can confirm by following the AWS document: View AWS account identifiers.
- Transit Gateway ID: The ID of your Transit Gateway to peer. The ID begins with
tgw-.
To create the Transit Gateway peering connection, follow these steps:
-
In the VPG settings page for the created VPG, click Closed Network > + Add Transit Gateway peering connection.
-
Configure the following settings:
- AWS Account ID
- Transit Gateway ID
- AWS Region
- Name (optional)
-
Click Add connection.
The Transit Gateway peering connection (Transit Gateway Peering Attachment) will be created.
-
You can see the following procedures for the configuration in the Peering Attachment Configuration window. Replace the following part of the AWS CLI command displayed under Accept Transit Gateway Peering Attachment and execute it on your workstation.
<REPLACE_YOUR_AWS_PROFILE>: Replace with your AWS CLI profile.
With the command, the Transit Gateway Peering Attachment of the Transit Gateway managed by Soracom will be accepted in your AWS account, and the following results will be displayed.
{ "TransitGatewayPeeringAttachment": { "TransitGatewayAttachmentId": "tgw-attach-xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx", "RequesterTgwInfo": { "TransitGatewayId": "tgw-xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx", "OwnerId": "000000000000", "Region": "sample-1" }, "AccepterTgwInfo": { "TransitGatewayId": "tgw-xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx", "OwnerId": "111111111111", "Region": "sample-2" }, "Options": { "DynamicRouting": "disable" }, "State": "pending", "CreationTime": "2024-XX-XXTXX:XX:XX+00:00" } }Initially, the status of the Transit Gateway peering connection on the page will be displayed as "pending". After the Transit Gateway Peering Attachment is accepted, it will change to "active".
Once you have created a Transit Gateway peering connection, you can see the "Transit Gateway Peering Settings" window again by clicking the Settings Icon next to Transit Gateway peering connections.
Configuring Routes
To enable bidirectional communication between the VPG and your Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) via the Transit Gateway peering connection, the following routing configurations are required:
- Routing from VPG to Your Amazon VPC
- Routing from Your Amazon VPC to Your Transit Gateway
- Routing from Your Transit Gateway to VPG
Routing from VPG to Your Amazon VPC
-
In the VPG settings page, click Routing Table > + Add Static Route.
-
Configure the following settings.
- Destination Network: Enter the CIDR block of your Amazon VPC.
- Gateway: Select the attachment ID of the Transit Gateway peering connection (Transit Gateway Peering Attachment) created in Creating a Transit Gateway Peering Connection. The VPC attachment ID can be displayed in the VPG settings page by clicking Closed Network Settings and then selecting Transit Gateway peering connections.
- Click Add.
Routing from Your Amazon VPC to Your Transit Gateway
-
Access the VPC Dashboard, switch to your region, and in the side menu, click Your VPCs.
-
Select your Amazon VPC, and click the route table ID displayed under Main Route Table.
-
Select the route table, go to the Routes tab, and click Edit routes.
-
Click Add route.
-
Configure the following settings.
- Destination: Enter the CIDR block for the VPG's device subnet IP address range. You can see this in the VPG settings page as Device Subnet IP Address Range.
- Target: Select "Transit Gateway" and enter your Transit Gateway ID. The ID begins with
tgw-.Ensure that the VPC route table is correctly associated with the subnet containing your EC2 instances. For VPCs with multiple subnets, verify that the desired subnet is explicitly mapped to the appropriate route table to avoid connectivity issues.
- Click Save changes.
Routing from Your Transit Gateway to VPG
-
Access the VPC Dashboard, switch to your region, and in the side menu, click Transit gateways > Transit gateway attachments.
-
Select the Transit Gateway peering attachment you created in the previous section, and under Association route table ID, click the route table ID to open it.
-
Click Routes > Create static route.
-
Configure the following settings:
- CIDR: Enter the IP address range of the device subnet for the VPG.
- Type: Select Active.
- Choose attachment: Select the attachment ID of the Transit Gateway peering connection (Transit Gateway Peering Attachment).
- Click Create static route.
Now the bidirectional communication between the VPG and your Amazon VPC is enabled.
Terminating the Transit Gateway Peering Connection
When you need to delete the Transit Gateway peering connection, follow these steps.
-
Delete static routes from the VPG routing table.
-
In the VPG settings page, click Routing table and click the button next to the static route where the Transit Gateway peering connection (Transit Gateway Peering Attachment) is specified as the Gateway.
-
Confirm and click Delete.
- If multiple static routes are configured for the Transit Gateway peering connection, delete all of them.
-
-
Delete the Transit Gateway peering connection (Transit Gateway Peering Attachment).
-
In the VPG settings page, click Closed Network and click the button next to the Transit Gateway peering connection (Transit Gateway Peering Attachment) to be terminated.
- Click Delete connection.
-
Even if you delete the Transit Gateway peering connection, the VPG usage fee will continue to be charged until the VPG is deleted. For more information about VPG usage fees, see Pricing & Fee Schedule. For details on terminating or deleting a VPG, see Terminating a VPG.
Be aware that you may also have to delete AWS resources such as EC2 and Transit Gateway to stop the charge if you do not need them.