Using Incoming Webhooks to Trigger Flux Apps
Incoming Webhook is a feature that issues a dedicated Webhook URL for sending events to Flux. By calling this URL, you can easily connect external systems to Flux apps.
The Incoming Webhook URL is generated by a channel in Flux. The URL can then be called from your applications or third-party applications to execute a Flux app.
Comparing Incoming Webhooks and API/Manual Execution Event Sources
An Event Source is a component that defines what events will trigger a Flux App to run.
An Incoming Webhook can trigger a Flux app to run and can be applied to any channel, initiating its downstream activities.
When sending data to a channel using the API/Manual Execution event source, you need an API Key and Token to interface with the API.
In contrast, using an Incoming Webhook allows you to send data without acquiring an API Key or Token, simplifying the process. Additionally, an Incoming Webhook can be generated from any channel in a Flux app.
| Event Source | Authentication | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| API/Manual Execution | Requires API Key and API Token | Controlled access to execute a Flux app |
| Incoming Webhook | No authentication required | Simplifies integration by allowing URL event triggering |
Security Warning: If the Incoming Webhook URL is exposed, unauthorized users may access it. Ensure it is securely managed and not shared publicly.
Creating an Incoming Webhook URL
- Sign in to the User Console. From the Menu, expand Soracom Flux and select Flux Apps.
- Open an existing Flux app or Create a Flux App.
- Click the channel where you want to create the Incoming Webhook or create a new channel.
- Select the Event Source tab and click the Create Incoming Webhook button.
-
Name the Incoming Webhook and optionally add a description, then click Create.
The Incoming Webhook URL will be created.
- Click Show Webhook URL to view it.
- Click to copy the URL, it will be needed to call the Flux app.
- To hide the Webhook URL, click Hide the webhook URL.
Each Flux app can issue up to 10 Incoming Webhooks.
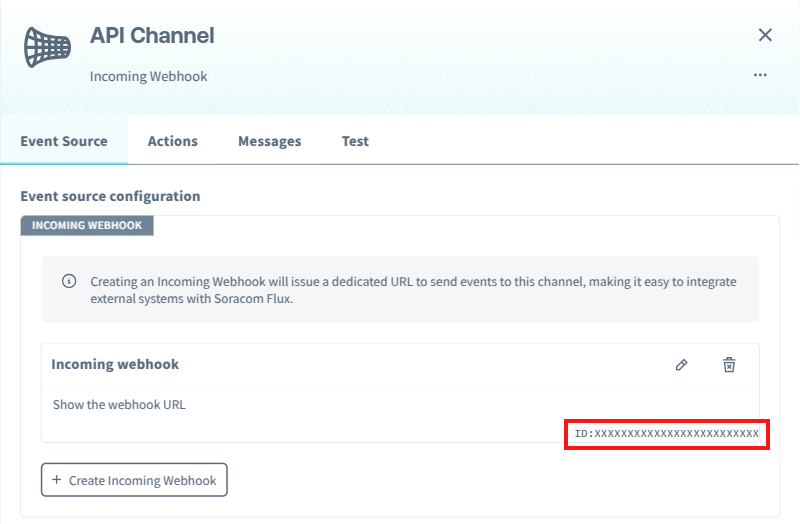
Each Incoming Webhook has a unique ID, displayed at the bottom right of the webhook settings. To view the ID, click on a channel where the webhook was created.
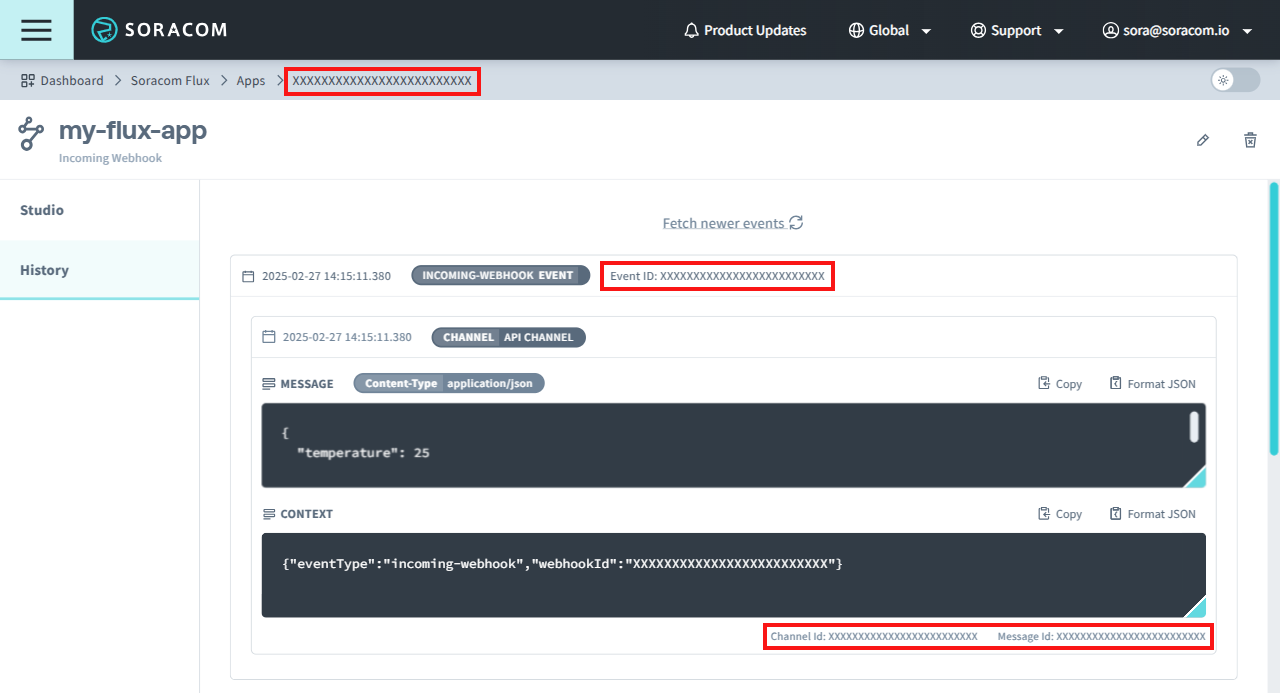
Data Sent to the Channel
When using Incoming Webhooks, two types of data are sent to the channel:
- Message: – The data payload (body) sent via the Webhook URL. The Flux app processes this payload.
- Context: – This contains metadata about the webhook event, such as the webhook ID and event type.
You can check the data received by a channel in a Flux app on the History Tab:
{
"eventType": "incoming-webhook",
"webhookId": "XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX"
}
Context Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
eventType |
Event type (incoming-webhook for Incoming Webhooks) |
webhookId |
Unique Incoming Webhook ID |
Invoking a Flux App via a Webhook URL
To invoke a Flux app, send an HTTP POST request to the Webhook URL.
- The Flux app starts execution from the channel associated with the Webhook URL.
Example: Sending a JSON Payload to the Webhook URL
This example simulates a request from a device and sends the payload {"temperature": 25} to a Webhook URL.
Request:
curl -X POST https://g.api.soracom.io/v1/flux/incoming_webhooks/XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX/XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"temperature": 25}'
The maximum payload size for a channel is 32,768 bytes. Any data exceeding this size cannot be sent.
Example Response
{
"messageId": "XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX",
"eventId": "XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX",
"appId": "XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX",
"channelId": "XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX",
"payload": {
"contentType": "application/json",
"content": "{\"temperature\":25}",
"isBase64Encoded": false
},
"context": {
"eventType": "incoming-webhook",
"webhookId": "XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX"
},
"timestamp": 1735689600000
}Response Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
messageId |
Message ID |
eventId |
Event ID (Viewable in History tab) |
appId |
Flux Application ID |
channelId |
Channel ID |
payload |
Data sent to the channel |
payload.contentType |
The Content-Type specified in the request header |
payload.content |
Data sent to the channel (Base64 encoded if applicable) |
payload.isBase64Encoded |
Indicates if payload was Base64 encoded |
context.eventType |
Event type (Always incoming-webhook for Incoming Webhooks) |
context.webhookId |
Incoming Webhook ID |
timestamp |
Timestamp of the event |
The messageId, eventId, appId, and channelId can be verified in the History tab to identify an event instance.