Overview
VPG Type F2 Now Available
The new VPG Type-F2 provides most of the same private networking, traffic control, and packet management features as Type-F but with substantially simplified private network configuration, fewer dependencies, and a lower total cost.
When Soracom Air for Cellular or Soracom Arc devices connect to the Soracom platform, core networking services are provided by a platform gateway. The default platform gateway allows Air and Arc devices to access Soracom services, such as Soracom Beam, Funnel, Funk, and Harvest Data/Files, as well as connect to the Internet.
As the default gateway is shared among all Soracom users, certain gateway functionality, such as private networking and device-to-device access, is disabled to ensure device and network security.
Soracom provides a Virtual Private Gateway (VPG) option which allows you to create and manage your own dedicated gateway on the Soracom platform. With a VPG, Air and Arc devices in your account connect to the Soracom platform using an isolated network environment, separate from other Soracom gateways.
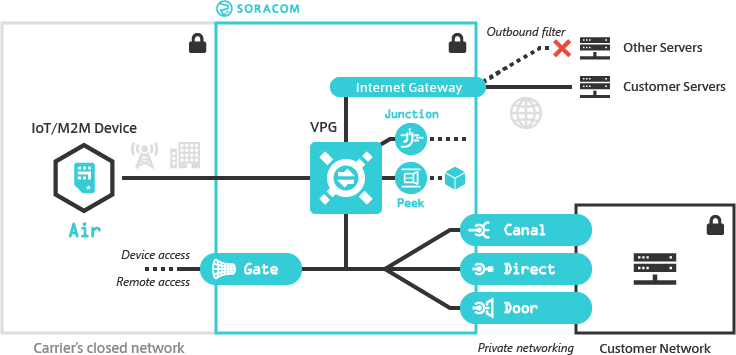
Since a VPG creates a dedicated network environment for your devices, you can in turn enable custom networking functionality such as device-to-device and remote access, control Internet access, connect devices directly to your private network, and perform packet management and inspection all within a closed secure network.
Features
Private Networking
As a VPG establishes a dedicated networking environment on the Soracom platform, you can connect the VPG to your private network using Soracom Canal, Door, or Direct. Once connected, Air and Arc devices attached to your VPG will be able to access resources in your private network, without routing traffic over the public Internet*1 or configuring firewalls to enable external access.
*1 - Soracom Door utilizes an IPsec VPN connection which may be routed over the Internet.
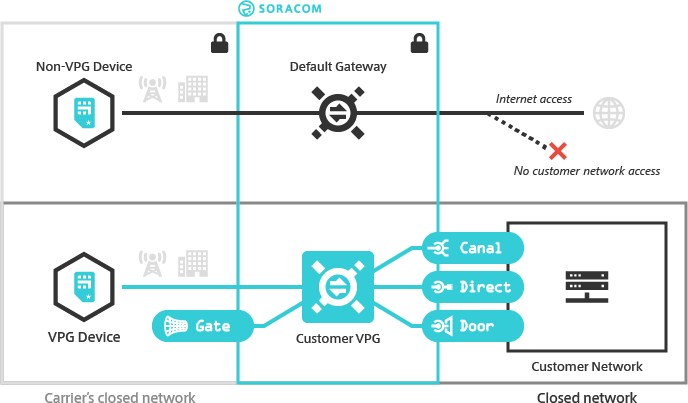
You can also enable Soracom Gate, which will allow Air and Arc devices attached to the same VPG to communicate with each other as if they were on the same LAN, no matter which country they are located in or what network they are connected to. When combined with Canal, Direct, or Door, this also allows devices in your private network to remotely access your devices.
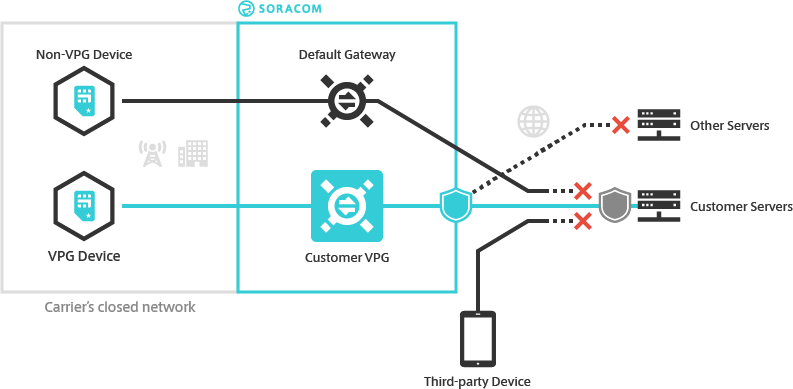
Since Air and Arc devices can communicate directly with servers in a private networking environment, you can also disable a VPG's Internet Gateway, effectively preventing any traffic from a device ever reaching the Internet.
For additional information on private networking functionality, refer to the VPG Type section below, or to the Soracom Canal, Door, Direct, and Gate documentation.
Traffic Routing Control
A VPG also lets you create custom traffic rules to control what network services your Air and Arc devices can reach. The Outbound Filter option lets you configure rules that allow your devices to connect to whitelisted servers, as well as rules that deny access to others.
The Fixed Global IP option lets you similarly control what traffic is allowed into your network. When enabled, your VPG will be assigned two dedicated static public IP addresses. You can then whitelist these IP addresses on your firewall in order to allow your devices to access your servers while blocking access from other Internet-connected devices.
For additional information, refer to the Outbound Filter and Fixed Global IP documentation.
Packet Management
With a VPG, you also get access to advanced packet management tools. Soracom Peek allows you to effortlessly capture packets that transit the VPG. This gives you the ability to inspect the network behavior of your Air and Arc devices before any traffic is routed to its destination, troubleshoot device communication problems, test your networking architecture, identify the source of high data usage, or improve security.
You can also use Soracom Junction to enable advanced packet handling, such as inspecting packets to perform traffic analysis, mirroring packets to observe real-time network behavior, or redirecting packets to apply your own traffic-shaping rules.
For additional information, refer to the Soracom Peek and Junction documentation.
Application Integration
As with the default platform gateway, devices connected to a VPG can also access Soracom application services, such as Beam, Funnel, Funk, and Harvest Data, in order to take advantage of each application's features while within the VPG's isolated network environment. For example, if your VPG is configured with Soracom Canal to establish a connection to your AWS VPC network environment, you can also use Soracom Beam to proxy data directly to an EC2 instance's private IP address or other VPC resources.
Using Soracom Beam MQTT and TCP → TCP/TCPS entry points with a public destination requires an Internet gateway route and therefore cannot be used with VPGs where the Internet Gateway option is disabled.
Normally, Soracom application services incur separate fees based on each service's pricing structure. However, as access to application services is built into each VPG and handled internally by the VPG's resources, you can use the following application services with a VPG without any additional cost:
- Soracom Beam
- Soracom Funnel
- Soracom Funk
- Custom DNS
- CHAP Authentication
Configuration Parameters
Type and Capacity
A VPG Type determines what networking services and options are available and can be configured, while its Capacity determines the number of concurrent sessions it is capable of handling. For applications where private networking capabilities are not required, the Type-E VPG provides most VPG features at an economical cost. The Type-F and Type-G VPGs provide the full set of private networking, traffic control, and packet management features, with the latter supporting over 100,000 concurrent sessions.
VPG Type-F2 provides most of the same private networking, traffic control, and packet management features as Type-F but with substantially simplified private network configuration, fewer dependencies, and a lower total cost.
| Service/Feature | Type-E | Type-F | Type-G *1 | Type-F2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concurrent Session Limit (Capacity) | Up to 1,000 | Up to 100,000 | Over 100,000 | Up to 100,000 | |
| Soracom Canal | |||||
| Soracom Door | |||||
| Soracom Direct | *2 | ||||
| Soracom Gate | *3 | ||||
*1 - Migrating from Type-F to Type-G is possible, however doing so will require resetting VPG settings and temporarily disconnecting devices. Because of this disruption, we recommend creating a Type-G VPG if you already expect the number of concurrent sessions to exceed the Type-F capacity.
*2 - Soracom Direct for Type-F2 utilizes a Transit VIF connection which is incompatible with the VIF connection utilized with Type-F and Type-G.
*3 - Cloud to Device access for Type-F2 can be configured without utilizing Soracom Gate.
Internet Gateway
The Internet Gateway provides routing from the VPG to public Internet infrastructure. When creating a Type-F, Type-G, or Type-F2 VPG, you can opt to disable the Internet Gateway to create a fully enclosed private network. In turn, you can use Soracom Canal, Direct, or Door to connect the VPG network environment to your private network, allowing your Air devices to access your servers.
The Internet Gateway setting cannot be modified after a VPG has been created. If you decide later to change the Internet Gateway behavior, you must create a new VPG.
The Internet Gateway is enabled by default for Type-E VPGs and cannot be modified. However, you can control what servers Air devices can access using the Outbound Filter option.
Rendezvous Point
When creating a Type-E, Type-F, Type-G, or Type-F2 VPG in the Global coverage region, you can select its Rendezvous Point which determines where the VPG network infrastructure is geographically located.
Rendezvous Points are so named as connections from Air and Arc devices attached to the VPG will be routed to this region. In effect, all cellular connections will first rendezvous at this location before continuing onward to your private network or to the public Internet, regardless of which countries the devices are located in or what networks they are connected to, in order to control latency or route sensitive data according to your application requirements.
Rendezvous Point cannot be configured for VPGs in the Japan coverage region - The Rendezvous Point will be set to Tokyo (Japan) and cannot be modified.
For additional information, refer to the Rendezvous Points documentation.
Device Subnet
Each VPG acts as a private network and assigns IP addresses to your Air and Arc devices according to a Device Subnet CIDR block. By default, a VPG will use the 10.128.0.0/9 IP address range, which can support a very large number of devices, with each device being uniquely addressable.
You can also specify a different Device Subnet CIDR block to use for your devices. This may be useful if the default range may cause collisions with an existing range in your private network.
Manually specified Device Subnets must be within the 10.0.0.0/8, 172.16.0.0/12, or 192.168.0.0/16 CIDR ranges and have a subnet mask of /24 or larger.
As Device Subnets represent a range of IP addresses that can be assigned to devices within your VPG, only network addresses can be specified. Host addresses cannot be used.
A Device Subnet range cannot be changed after a VPG has been created.
Additional Properties
Each VPG will also be assigned a VPG IP address range within the 100.64.0.0/10 (RFC 6598: Shared Address Space) CIDR block. This IP address range is automatically assigned by Soracom and are used to establish redundancy in the underlying network infrastructure through AWS Availability Zones, as well as for inter-network connectivity.
The VPG IP address range corresponds only to the underlying network infrastructure and is separate from the Device Subnet as well as the external IP address where traffic from your devices will originate.
Type-E VPGs and Type-F, Type-G, and Type-F2 VPGs with the Internet Gateway enabled will also act as a NAT using this IP address range (sometimes referred to as CGNAT) to provide Internet connectivity.
In most cases, the VPG IP address range is not required for most VPG functionality. However, when configuring Soracom Gate Remote Access for Type-F and Type-G VPGs, you will need to refer to this IP address range in order to perform Gate Peer configuration so that traffic from your private network can be correctly routed to the VPG.
For Type-F2 VPGs, while the VPG IP address range will still be used for the underlying network infrastructure and for acting as a NAT for Internet connectivity, this range is not required for configuring remote device access from your private network.
Additional Gateways
In addition to a fully customizable VPG, Soracom provides additional gateways called Private Garden and Public Gate, which enable common networking functionality not possible with the default shared platform gateway. As these additional gateways are also shared among all Soracom users, there are certain limitations and precautions, however, they allow certain use cases without the need to create and configure a dedicated VPG.
Private Garden
The Private Garden provides similar network connectivity as the default shared gateway but with Internet-bound traffic blocked. IoT SIM devices that are configured to use the Private Garden gateway are still able to access Soracom services, such as Beam, Funnel, Funk, Harvest Data.
When your application utilizes Beam, Funnel, Funk, or Harvest to send or capture data, Private Garden provides an additional layer of security, ensuring that in the event a device is exploited, any attempts to communicate with external servers over the Internet will be blocked.
Although the Private Garden must be selected for use, it is similar to the default shared gateway in that connectivity is shared among all IoT SIMs that are attached to the Private Garden, including IoT SIMs from other Operators. Similarly, remote access and device-to-device access is blocked, and connecting to other private networks is not supported.
For additional information, refer to the Private Garden documentation.
Public Gate
Some applications may require a device to be able to communicate with another device. While Soracom Gate enables implicitly secure device-to-device communication by using a dedicated VPG, Soracom Gate configuration may be excessive for simple applications such as sending an OK message from one device to another.
The Public Gate provides similar network connectivity as the default shared gateway but enables device-to-device communication. Once two or more devices have been configured to use the Public Gate, they can communicate with each other by using their IP addresses.
When using Public Gate, keep in mind that network connectivity is similar to the default shared gateway in that connectivity is shared among all IoT SIMs that are attached to the Public Gate, including IoT SIMs from other Operators. As a result, devices from other Operators are able to communicate with your devices, much like when a device is connected to public wifi. Ensure that you change any default passwords (such as operating system users, SSH, and web-based management interfaces), disable or remove unnecessary network services, and use appropriate mechanisms for verifying connections.
In order to ensure device security, we recommend using Public Gate with non-sensitive data, or for application testing only.
For additional information, refer to the Public Gate documentation.